by Mike Rogan, Rhodes University; Max Gallien, Institute of Development Studies; Nana Akua Anyidoho, University of Ghana, and Vanessa van den Boogaard, Institute of Development Studies
In May 2022, the government in Ghana introduced a deeply unpopular tax on mobile money transactions, known as the e-levy. When it was introduced, the levy was structured as a 1.5% charge on all electronic and mobile money transactions over 100 cedis per day.
The e-levy was designed to raise more money for the government by extracting larger tax contributions from Ghana’s informal sector. About 90% of total employment in Ghana is informal and politicians have explicitly stated that the e-levy is targeted at the informal sector.
In January 2023, the government reduced the rate of the tax from 1.5% to 1%. The unique feature of the levy, an exemption threshold for transactions below 100 cedis a day, is expected to be removed but remains in place for now, although it’s real value has been eroded by inflation over the past 12 months.
The levy’s effects – on Ghana’s public finances, its poor, mobile money usage –have been at the centre of intense and polarising public conversations, much of it without empirical basis.
In September 2022 we presented some early results from a survey of 2,700 self-employed informal sector operators, carried out just before the introduction of the e-levy, where we showed the likely impact of the tax on Accra’s informal sector.
In our recent paper we assess how informal sector operators in the country’s capital Accra use mobile money. We also asked the views of informal workers on what they thought of the e-levy’s pending implementation.
Our findings suggest that the e-levy is highly regressive. In other words, our data show that the lowest earning informal sector operators pay a larger share of their earnings towards the levy than higher earners. We also show that most informal workers disapprove of the e-levy.
Our findings suggest that the government should reconsider the design of the e-levy to ensure that the most vulnerable workers in the informal sector are protected. We suggest further that the exemption threshold for low value transactions is an important tool in this regard and should be retained for the sake of equity.
Lower rate brings relief
What does the lowered rate of 1% mean for informal workers? In our recent study, we analysed information on the use of mobile money transactions among informal sector operators in Accra. We divided informal sector operators into five equal groups (quintiles), based on their reported earnings. Before the lower rate of 1% was introduced in January 2023, we calculated that e-levy payments would amount to about 4% of reported monthly earnings for the lowest earning quintile. The tax would amount to less than 1% for the two highest earning quintiles.
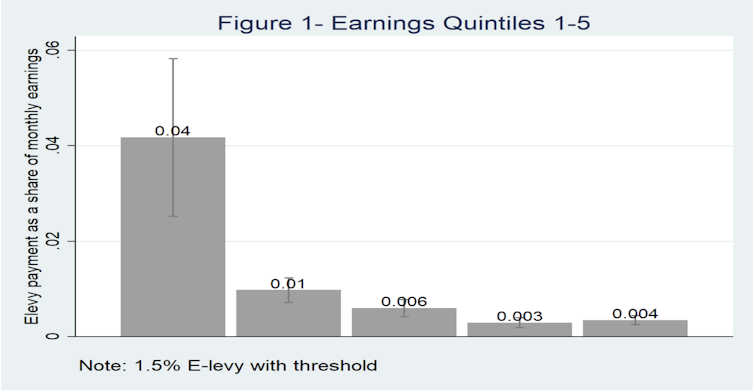
This shows that the levy takes more from the poorest. And the lowest earners pay a substantial portion of their already meagre earnings towards the levy.
The lower rate brings a small degree of relief for the lowest earners. When the new e-levy rate (1%) is mapped onto our survey data, the lowest earning quintile would pay about 3% (instead of 4%) of their monthly earnings towards this tax, all else remaining equal.
Threshold an important tool for the poor
If the protective threshold were to be removed–in line with the recent budget statement–the lowest earning quintile would pay, on average, 7% of their monthly earnings towards the e-levy. In other words, even at the new lower rate, the removal of the exemption threshold would more than double the liability of the poorest informal sector operators.
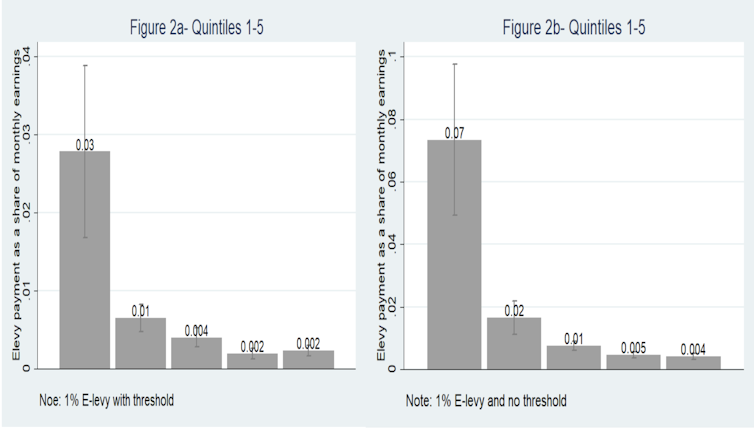
The transfer threshold therefore appears to be an important instrument for protecting the lowest earning operators, irrespective of the rate at which the levy is set. But due to inflation, the real value of the threshold, as of January 2023, has been eroded by more than 50%. In other words, the threshold is now only half as effective at shielding the poorest as it was to start with.
Next steps
As mobile money taxes gain popularity across the continent, their design requires very careful consideration. Currently there are at least ten African countries that are either considering, or have implemented, a similar tax.
Our research suggests that efforts to protect the poorest mobile money users (often the unbanked working in the informal sector) should be the priority. We further argue that Ghana’s use of a protective threshold is an important feature of the policy design–more important than, for example, simply lowering the rate–but that it doesn’t go far enough to protect the poor.
More fundamentally, we reflect on the effectiveness of the tax from a revenue perspective. The new tax measure has performed much more poorly in revenue terms than the government had hoped for. In first 8 months of the levy’s introduction, it raised only 11% of its revenue target of US $1 billion.
It is therefore worth asking what else the government can do to meet its pressing revenue needs. There is substantial evidence that focusing on higher income earners, including high net worth individuals and extractive industries, can be particularly productive. The development of a unit in the Ghana Revenue Authority that focuses on wealthy individuals is a promising step in this direction, though the outcomes of these efforts remain to be seen.
The experience of the e-levy so far offers important lessons to other countries considering similar taxes. Among the most important is that domestic resource mobilisation cannot be achieved by over-taxing the livelihoods of the most vulnerable workers in the informal sector.![]()
Mike Rogan, Associate Professor, Rhodes University; Max Gallien, Research Fellow, Institute of Development Studies; Nana Akua Anyidoho, Associate Professor & Director, Centre for Social Policy Studies, University of Ghana, and Vanessa van den Boogaard, Research Fellow, Institute of Development Studies
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
